Supporting Social-Emotional Development at Mt. Sinai CDC

The Importance of Social-Emotional Development
Social-emotional development is one of the most crucial aspects of early childhood growth. It influences how children manage their emotions, build relationships, make decisions, and navigate the challenges of everyday life. At Mt. Sinai Children’s Development Center (CDC), we believe that fostering strong social-emotional skills in the early years lays the foundation for success not only in school but also in life. Social-emotional development helps children understand themselves, empathize with others, and manage their feelings in healthy ways.
In this blog post, we will explore the various strategies Mt. Sinai CDC employs to support social-emotional development. From providing a nurturing environment to teaching children conflict-resolution skills, we are dedicated to helping every child develop the emotional intelligence they need to thrive.
1. Building Emotional Awareness
The first step in social-emotional development is helping children understand their own emotions. Before children can regulate their emotions, they need to be able to recognize and name what they are feeling. At Mt. Sinai CDC, we help children develop emotional awareness through a variety of activities and teaching methods.
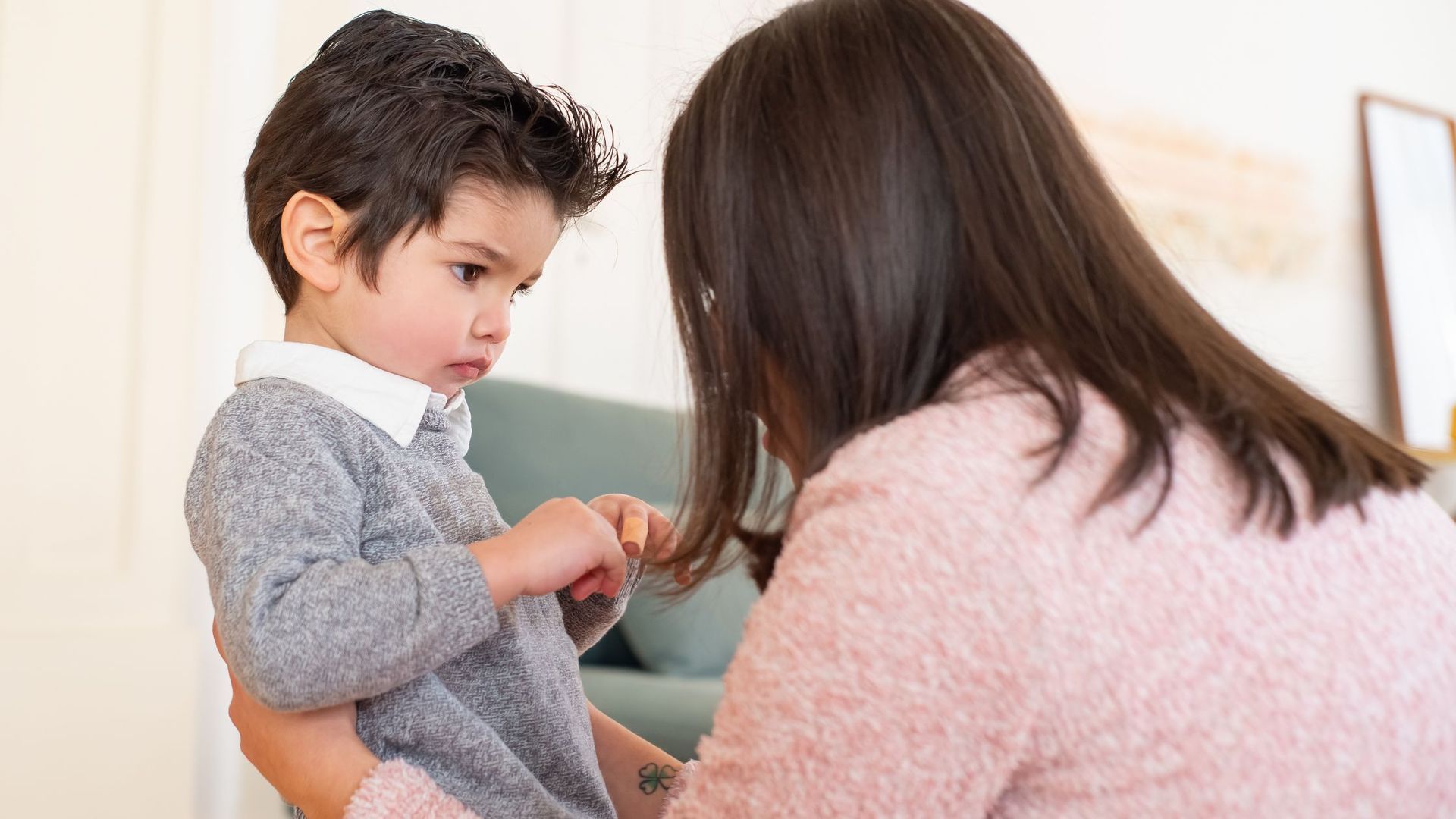
- Identifying Emotions: We introduce children to a wide range of emotions through activities that encourage them to recognize and label their feelings. Using tools like emotion charts, picture books, and role-playing activities, children learn about different emotions, such as happiness, sadness, anger, and fear. By discussing emotions openly, we help children understand that all feelings are valid and can be expressed in healthy ways.
- Talking About Feelings: Creating a safe space where children can talk about their feelings is key to emotional awareness. At Mt. Sinai CDC, our teachers encourage children to verbalize their emotions and express what they are feeling in a supportive environment. For example, if a child is upset, the teacher might ask, “How are you feeling today?” or “Can you tell me why you are sad?” These conversations help children connect their emotions to their behavior and understand the reasons behind their feelings.
- Using Books and Stories: Picture books are an excellent way to help children explore different emotions. Stories that focus on characters dealing with various feelings allow children to see how others navigate emotions and give them a safe way to explore their own feelings. We choose books that reflect a wide range of emotions, allowing children to relate to the characters and deepen their understanding of emotions.
By teaching children to identify and name their emotions, we provide them with the tools they need to understand their feelings and begin the process of emotional regulation.
2. Developing Emotional Regulation Skills
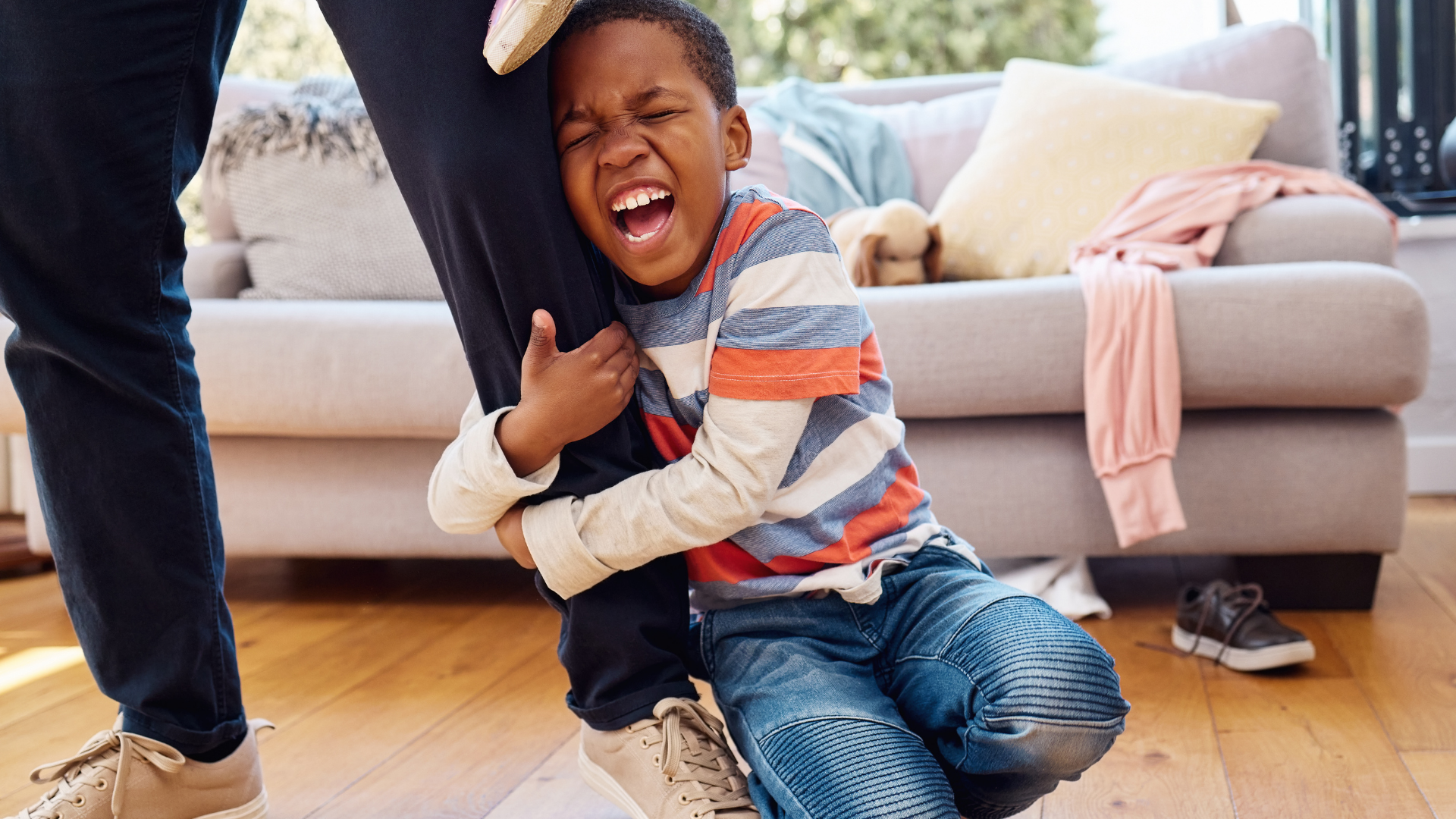
Emotional regulation is the ability to manage and control one’s emotions in a healthy way. Learning to regulate emotions is a lifelong process, but the early years are crucial for laying the foundation for this skill. At Mt. Sinai CDC, we focus on teaching children how to cope with difficult emotions, such as frustration, anger, or anxiety.
- Calming Strategies: We teach children various techniques to help them calm down when they are feeling upset. Simple strategies like deep breathing, counting to ten, or taking a break in a quiet space help children learn to manage their emotions. For example, when a child feels angry, we might suggest, “Let’s take three deep breaths together” or “Try counting slowly to ten.” These strategies help children develop self-regulation skills and build resilience when faced with emotional challenges.
- Modeling Emotional Regulation: Children learn a great deal by observing the behavior of adults around them. Our teachers model emotional regulation by calmly handling their own emotions and demonstrating appropriate ways to cope with stress. When a teacher faces a frustrating situation, they might say, “I’m feeling frustrated, so I’m going to take a deep breath to calm down.” By modeling these behaviors, we help children understand that it’s okay to feel upset, but it’s important to manage those feelings in a constructive way.
- Role-Playing Scenarios: Role-playing is an effective way to help children practice emotional regulation. We create scenarios where children can act out different situations, such as taking turns, sharing, or expressing frustration. These role-playing activities give children the opportunity to practice using calming techniques in real-life situations, building their emotional regulation skills.
By teaching children calming strategies and providing opportunities to practice emotional regulation, we help them develop the self-control and resilience they need to handle their emotions effectively.
3. Building Empathy and Social Skills
Social-emotional development is not just about understanding and managing one’s own emotions; it also involves developing the ability to understand and relate to the emotions of others. Empathy, the ability to recognize and understand the feelings of others, is an essential social-emotional skill that lays the foundation for healthy relationships.
- Teaching Empathy: We teach children to recognize the emotions of others by discussing how their peers might be feeling in different situations. For example, if a child is crying, we might ask, “How do you think they are feeling? What can we do to help them feel better?” These discussions help children develop empathy by encouraging them to think about others' feelings and perspectives.
- Modeling Empathy: Just as with emotional regulation, children learn empathy by observing adults. Our teachers model empathetic behaviors by offering comfort and support to children who are upset or in need of assistance. For example, when a child helps a friend pick up toys or comforts a peer who is feeling sad, the teacher might say, “That was very kind of you to help your friend feel better.” These positive interactions help children understand the value of empathy and kindness.
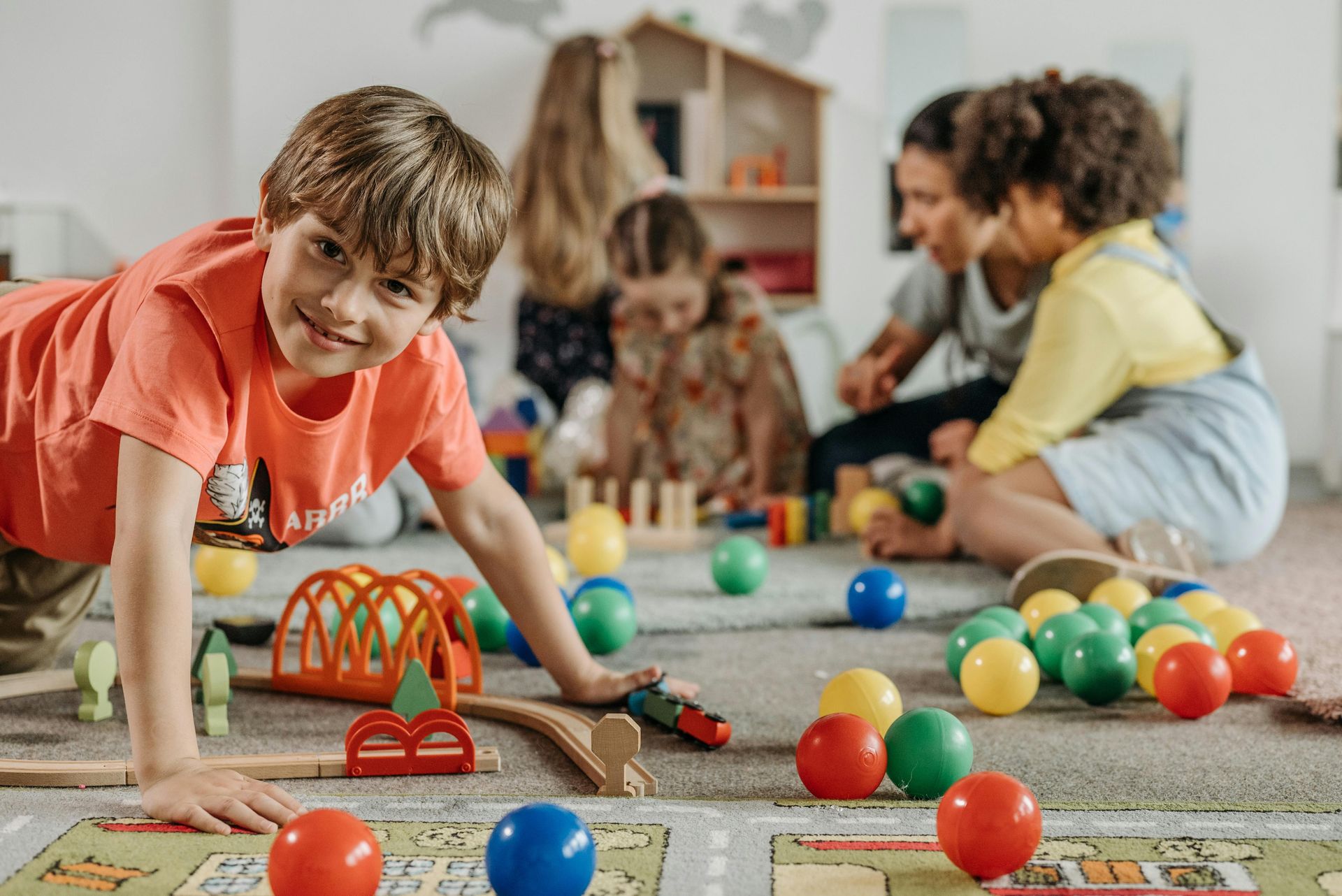
- Cooperative Play and Social Interaction: Play is one of the most effective ways for children to develop social skills and practice empathy. By engaging in cooperative play activities, children learn how to share, take turns, and communicate with others. Whether it’s working together to build a tower with blocks or playing a game of “Simon Says,” cooperative play helps children practice the social skills needed to form positive relationships with their peers.
At Mt. Sinai CDC, we create numerous opportunities for children to interact with others and practice their social skills. Through group activities, playtime, and guided discussions, we foster empathy and teach children the importance of kindness, cooperation, and respect.
4. Conflict Resolution and Problem-Solving
Conflicts are a natural part of life, and learning how to resolve conflicts in a positive way is an important social-emotional skill. At Mt. Sinai CDC, we teach children effective strategies for solving problems and resolving conflicts with their peers. These skills are essential for building healthy relationships and promoting a positive social environment.
- Teaching Conflict Resolution: We teach children to handle conflicts calmly and respectfully by using “I” statements, such as “I feel upset when you take my toy. Can we take turns?” This allows children to express their feelings without blaming others. We also encourage children to listen to each other’s perspectives and work together to find a solution that satisfies everyone involved.
- Guided Problem-Solving: When conflicts arise, our teachers guide children through the problem-solving process by asking questions like, “What happened?” “How did that make you feel?” and “What can we do to solve this problem?” These discussions help children think critically about the situation and come up with creative solutions. By teaching children to approach conflicts as opportunities to learn and grow, we help them develop the skills they need to handle disagreements in a constructive way.
- Role-Playing Conflict Scenarios: Just as with emotional regulation, role-playing is an effective way for children to practice conflict resolution. We create scenarios where children can practice resolving conflicts in a safe, guided environment. These role-playing activities help children learn how to communicate their needs, negotiate with others, and resolve conflicts peacefully.
Through teaching conflict resolution and problem-solving, we empower children to navigate challenges and build positive, respectful relationships with their peers.
5. Creating a Nurturing and Supportive Environment
At Mt. Sinai CDC, we believe that a nurturing, supportive environment is essential for social-emotional development. When children feel safe, valued, and respected, they are more likely to develop positive social-emotional skills. Our teachers work hard to create an environment that promotes emotional well-being, kindness, and cooperation.
- Establishing Trust: Trust is the foundation of any healthy relationship, and we prioritize building trust with the children in our care. Our teachers take the time to get to know each child, listen to their needs, and respond with care and empathy. This trust allows children to feel secure and confident in their ability to express themselves and seek help when needed.
- Promoting Positive Reinforcement: We celebrate children’s efforts and achievements, no matter how big or small. Positive reinforcement helps build children’s self-esteem and encourages them to continue practicing social-emotional skills. When a child demonstrates empathy, cooperates with others, or successfully regulates their emotions, we offer praise and recognition to reinforce these behaviors.
- Fostering a Sense of Belonging: We create a sense of belonging by promoting a culture of inclusion and respect. Every child is encouraged to participate, share their thoughts, and contribute to the classroom community. By celebrating diversity and promoting respect for others, we help children develop a sense of pride in themselves and their peers.
At Mt. Sinai CDC, we prioritize
promoting health and wellness in early childhood to help children develop strong foundations for lifelong well-being and success.
Supporting Social-Emotional Growth at Mt. Sinai CDC
At Mt. Sinai CDC, we are committed to supporting the social-emotional development of every child. By teaching emotional awareness, regulation, empathy, and conflict resolution skills, we help children build the foundation for healthy relationships, resilience, and success. Our nurturing environment and dedicated teachers provide children with the tools they need to understand themselves, navigate social situations, and become compassionate, confident individuals.